The cloud is our future. We have fundamentally no choice.
—Satya Nadella, CEO Microsoft
Enabling Business Agility with the Cloud and SAFe®
Note: This article is part of Extended SAFe Guidance, and represents official SAFe content that cannot be accessed directly from the Big Picture.
The ever-expanding universe of cloud capabilities has fundamentally changed the way digitally enabled solutions are built, deployed, and maintained. In fact, cloud computing is the single most disruptive driver of delivery model change that enterprise IT has faced since its inception [1]. Not surprisingly, the number one reason enterprises are moving to the cloud so quickly is to increase product development speed and agility [2].
The cloud is everywhere, and it fuels digital business. SAFe enterprises can harness the power and ubiquity of the cloud to increase agility in all areas of the organization.
Details
As the cloud has evolved from a technology disruptor to a business disruptor [3], it now permeates all facets of the enterprise. It supplies computing resources on-demand to IT operations and engineering teams. It provides professionals across business functions with fast, reliable access to applications that boost collaboration and productivity. It enables the artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities that allow enterprises to achieve major advancements in product innovation.
Digitally savvy enterprises leverage cloud capabilities to not only transform how their technology is managed but how they deliver new products to market. The result is an enterprise that responds quickly to dynamic market forces and engineering teams that serve as value engines for the business. This is achieved by combining cloud capabilities with Lean-Agile practices in key Development Value Streams (DVS).
Aligning the Cloud to Value
When the cloud is used to host enterprise systems, those systems run more reliably and are maintained more efficiently. This transforms the technology landscape and can reduce operating costs. But when cloud capabilities are also used to enable the DVS (Figure 1), innovation is accelerated. This transforms the business landscape and can generate new value quickly and continuously for the enterprise.
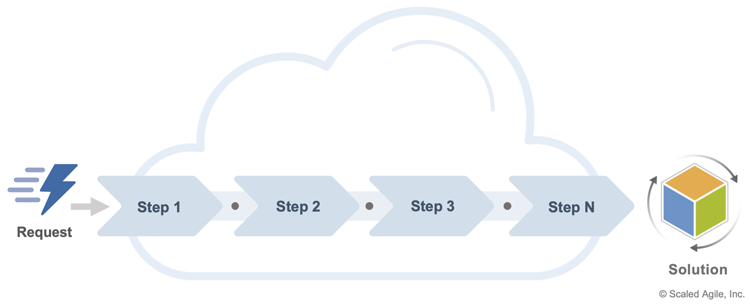
By aligning cloud capabilities with value-generating activities, enterprises maximize their ability to experiment quickly and deliver disruptive solutions to their markets.
There exist innumerable cloud strategies and implementation models, each of which has unique benefits. Among them are three common patterns that work together with SAFe to enable enterprise-scale agility. Here, they are characterized as Cloud for Infrastructure & Operations (I&O), Cloud for DevOps, and Cloud for AI (Figure 2).
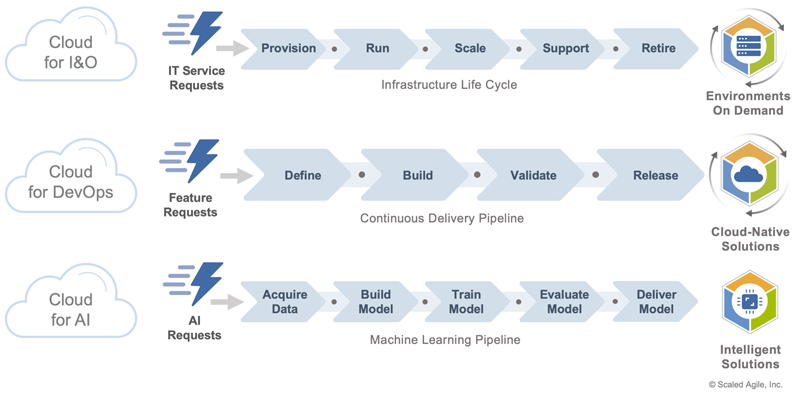
Each of these patterns enables a unique DVS. Each DVS combines cloud capabilities with SAFe to deliver transformational innovation to a specific set of customers. Together, they scale operational efficiencies and business agility throughout the enterprise.
The first, and most foundational, of these patterns is Cloud for I&O.
Cloud for Infrastructure and Operations
Cloud for I&O is a rehosting pattern that often begins with migrating business solutions from on-premises data centers to the cloud. It automates the end-to-end infrastructure life cycle and delivers runtime environments that can be provisioned, scaled, and retired on demand. This significantly accelerates flow from infrastructure ‘request’ to ‘retire,’ alleviating common bottlenecks stemming from long service request lead times.
Figure 3 illustrates the Cloud for I&O pattern, depicting the key inputs, workloads, outputs, and architecture that increase the speed and agility with which core IT services and infrastructure are managed.
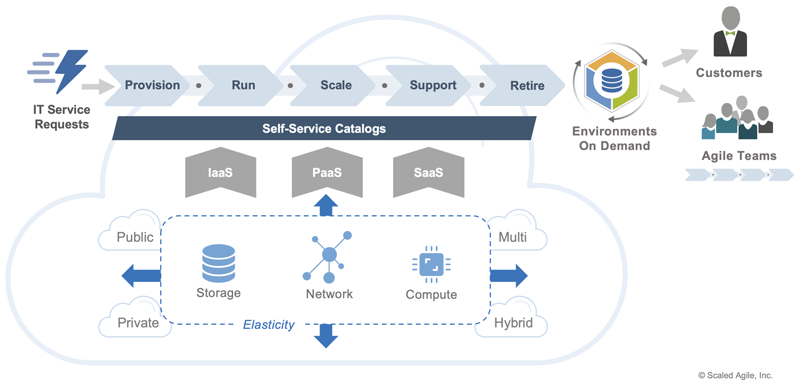
Inputs – The I&O cloud scenario begins with a service request for storage, network, or compute resources to support the deployment or production maintenance of a software-based business solution. Web-based, self-service catalogs expose secure, compliant resources directly to the requesting individual or team, allowing them to fulfill their own infrastructure needs quickly.
Workloads – The I&O cloud runs production workloads, such as the automated provisioning of application and database servers, executing application runtime containers, scaling hardware capacity for fault tolerance, administering security patches and maintenance updates, and retiring legacy infrastructure. Tasks that have historically been performed with long lead times by small teams of system administrators with elevated access privileges are performed in near real-time by automated cloud services.
Outputs – The I&O cloud delivers on-demand access to production resources and their configurations. This benefits Agile Teams by reducing, if not eliminating, service request lead times. It benefits business stakeholders by shifting the complexities of data center management to the cloud provider.
Architecture – The I&O cloud consists of physical and virtual machines that provide highly elastic (horizontally and vertically scalable) storage, networking, and computing services. This infrastructure is hosted by the cloud provider and is exposed via self-service websites as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS) capabilities. The I&O cloud can be implemented in public cloud, private cloud, multi-cloud, and hybrid cloud configurations.
How SAFe helps – Cloud for I&O requires that an organization’s technical cloud strategy is tightly aligned with its need to deliver continuous, sustainable business value. Datacenter migration, rehosting, and ‘lift and shift’ initiatives, therefore, must yield not only reliable hosting environments for business solutions but services that enable those environments to be configured, scaled, and reconfigured rapidly in response to changing business needs. SAFe enables this technology-business alignment in the following ways:
- Customer centricity – Enterprise Architects, Solution Architects, System Architects, and Product Management collaborate closely to ensure that the I&O cloud is organized around value and designed to deliver the services that Agile teams and internal stakeholders need to realize significant productivity gains and economic benefits.
- Strategic alignment – Technical strategy and business strategy remain in lockstep via Strategic Themes, Lean Budgets, Enablers, and PI Objectives that are shared across the organization.
- Incremental delivery – Through adherence to Principle #4 – Build incrementally with fast, integrated learning cycles, the I&O cloud delivers a continuous flow of value as it evolves, rather than delaying all functionality to the completion of a ‘big bang’ conversion.
- Agile operations – SAFe integrates I&O teams with Agile Release Trains (ARTs), fostering cross-functional collaboration and the development of an organization-wide, Lean-Agile culture.
Cloud for DevOps
Cloud for DevOps involves shifting these I&O services ‘left’ into the delivery pipeline. This allows Agile teams to set up, use, and tear down secure, compliant cloud-based resources in support of continuous solution innovation. With this pattern, solutions are redesigned using cloud-native technology and delivered as modernized, next-generation products and services, either to be consumed directly by customers or integrated into larger solutions.
As depicted in Figure 4, this is a composite pattern that incorporates Cloud for I&O as a critical enabler.
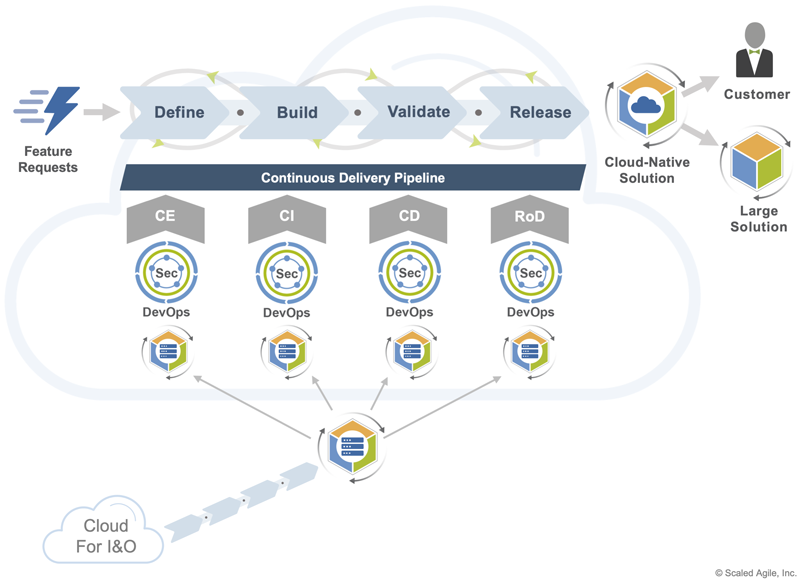
Inputs – The arrival of one or more feature requests in the Program Backlog triggers this value flow, which in turn initiates the Continuous Delivery Pipeline. Typically, these requests are for features meant to optimize existing solutions for the cloud or deliver net-new experiences.
Workloads – The DevOps cloud runs workloads that support the end-to-end solution delivery life cycle, such as Agile planning and design, low-code and no-code development, CI/CD, version control, application telemetry, security-as-code, and other activities described by SAFe’s DevOps Practice Domains. These workloads automate the Continuous Delivery Pipeline and provide Agile teams and ARTs the on-demand resources they need to build and sustain team and technical agility.
Outputs – This pattern greatly accelerates feature delivery (often by orders of magnitude), generating high-quality, cloud-native solutions that offer competitive differentiation in the market. These are loosely coupled, containerized solutions that can be scaled and modified quickly to fuel continuous innovation. These outputs are used directly by end-users or integrated into other solutions, including Large Solutions.
Architecture – The I&O cloud makes storage, network, and compute environments available for use throughout the development value stream. This supplies Agile teams and ARTs with the infrastructure, applications, and DevOps capabilities required to fuel Continuous Exploration (CE), Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Deployment (CD), and Release on Demand (RoD) activities.
How SAFe helps – This pattern provides much of the tooling necessary to implement a continuous delivery pipeline and enable DevOps. However, effective DevOps involves more than automation. Combined with Cloud for DevOps, SAFe can ensure that organizations are working collaboratively across functions in the following ways to continuously deliver value:
- A CALMR approach to DevOps – Guided by systems thinking, SAFe provides an approach to DevOps that builds a culture of continuous delivery. Culture, automation, lean flow, measurement, and recovery are all elements of the DevOps mindset that SAFe keeps balanced throughout development, operations, and the business.
- DevOps Practice Domains – SAFe provides a comprehensive reference model that defines the practices and tools that fuel continuous delivery. These are the services that should be implemented in the DevOps cloud and frequently assessed for quality using the DevOps Health Radar.
- Agile Product Delivery (APD) – As one of SAFe’s seven core competencies of the Lean enterprise, APD combines DevOps with customer-centricity, design thinking, and cross-functional Agile cadence. APD ensures that the DevOps cloud is calibrated to deliver valuable solutions in the shortest sustainable lead time.
- Built-in Quality (BiQ) – Much of the value of the DevOps cloud is in its ability to shift operations capabilities left to ensure high quality and fast flow through the delivery pipeline. SAFe’s BiQ practices ensure that the DevOps cloud exposes services that enforce design, code, system, and release quality.
Cloud for AI
Cloud for AI enables enterprises to reinvent their solutions to achieve new levels of competitive advantage. It provides the massive computing power required to fuel the development of sophisticated machine learning models, which drive intelligent, AI-based solutions that generate new value for the business.
Like cloud for DevOps, Cloud for AI is a composite pattern that extends the capabilities of the I&O cloud (Figure 5).
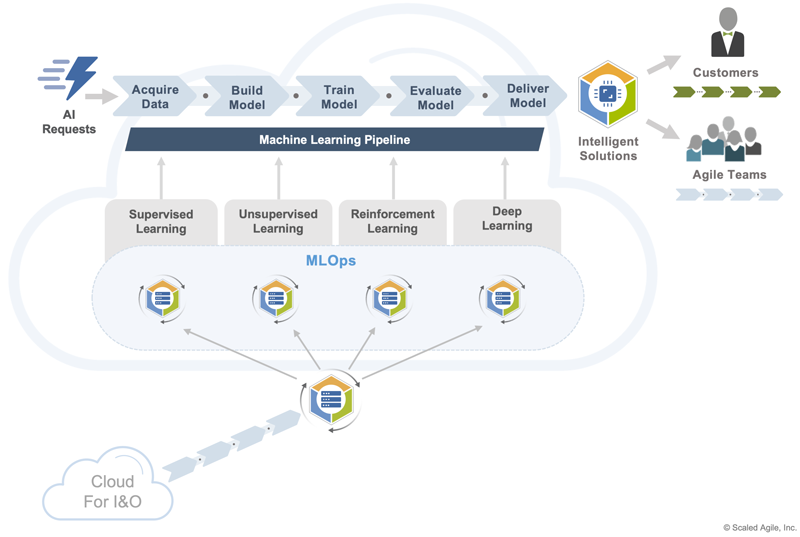
Inputs – This development value stream begins with the need for an AI-driven solution. It could be captured as an Epic, Feature, Capability, or Story and represents a business-focused opportunity to deliver an intelligent customer-facing solution, improve value stream efficiency, or gain insights about customers and markets.
Workloads – The AI cloud runs workloads that enable the development of machine learning models through a highly iterative machine learning pipeline. This includes workloads that assist with acquiring and mapping data sets, developing and training machine learning algorithms, evaluating algorithms for accuracy, and integrating and delivering the finished models. These workloads support the development of the four fundamental types of AI—supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement, and deep learning—through an iterative, collaborative machine learning operations (MLOps) process that involves data scientists and AI engineers.
Outputs – This pattern produces intelligent, AI-driven solutions that address a variety of needs both inside and outside the enterprise. External customers benefit from more intelligent and engaging AI solutions, internal stakeholders benefit from AI-generated market insights, and Agile teams benefit from AI-driven enhancements to development and Operational Value Streams.
Architecture – The I&O cloud supplies the storage, network, and compute resources needed to execute the machine learning pipeline. These typically consist of big data environments and compute resources powered by graphical processing units (GPUs) that can handle the high data volumes and processing power required to develop ML models. These resources are orchestrated by data scientists and ML engineers into an MLOps process that rapidly and iteratively advances the solution through the pipeline.
How SAFe helps – As explained in the advanced topic article, Succeeding with AI in SAFe, AI offers enterprises the opportunity to significantly increase competitive advantage and achieve better business outcomes. But operationalizing and scaling this advanced, disruptive technology requires sophisticated cloud capabilities. SAFe helps organizations build and operate a reliable, value-aligned AI cloud in the following ways:
- AI decision-making framework – SAFe enables enterprises to make informed decisions about the AI cloud services that would serve them best through strategic alignment, customer centricity, continuous exploration, and empirical milestones.
- Scaling AI capabilities – Through Principle #10 – Organize around value, SAFe helps enterprises align their AI clouds to business needs. SAFe also facilitates the rapid dissemination of AI cloud expertise throughout the organization via cross-functional Agile teams, communities of practice, and numerous synchronization events that accelerate knowledge acquisition and sharing.
- Enabling business agility – SAFe orients the entire organization to a unified mission of building Business Agility—the ability to sense and respond to market opportunities with winning business solutions. Everyone involved in operationalizing the AI cloud, from data scientists and AI engineers to cloud architects and product managers, must be united in their focus on increasing overall business agility.
- Managing big data – Data is the lifeblood of the AI cloud, but the complex infrastructure required to manage the storage, distribution, and quality of that data can create bottlenecks in the machine learning pipeline. As described in An Agile Approach to Big Data in SAFe, SAFe provides guidance and tools for maintaining flow via Agile data teams, an iterative DataOps pipeline, portfolio-level support and funding, and federated data governance.
Summary
More and more, enterprises are turning to the cloud to create the agility they need to survive and thrive in the digital age. However, simply migrating enterprise systems from on-premises data centers to the cloud is not enough. They must also leverage the cloud to automate and accelerate value-generating activities across the organization.
Cloud for I&O, Cloud for DevOps, and Cloud for AI align an enterprise’s cloud implementations with the development value streams that deliver disruptive digital innovation, combining powerful cloud services with SAFe principles and practices to enable true business agility.
Learn More
[1] Abdula, Moe, Ingo Averdunk, Roland Barcia, Kyle Brown, and Ndu Emuchay. The Cloud Adoption Playbook: Proven Strategies for Transforming Your Organization with the Cloud. Wiley, 2018. [2] Orban, Stephen. Ahead in the Cloud: Best Practices for Navigating the Future of Enterprise IT. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2018. [3] Gartner. Predicts 2022: The Cloud Moves from Technology Disruption to Business Disruption, 2021. https://www.gartner.com/doc/4008904.
Last Update: 19 April 2022






